According to the latest World malaria report, there were 245 million cases of malaria in 2020. The estimated number of malaria deaths stood at 625 000 in 2020.
Over the 2 peak years of the pandemic (2020–2021), COVID-related disruptions led to about 13 million more malaria cases and 63 000 more malaria deaths. The WHO African Region continues to carry a disproportionately high share of the global malaria burden. In 2021 the Region was home to about 95% of all malaria cases and 96% of deaths. Children under 5 years of age accounted for about 80% of all malaria deaths in the Region.
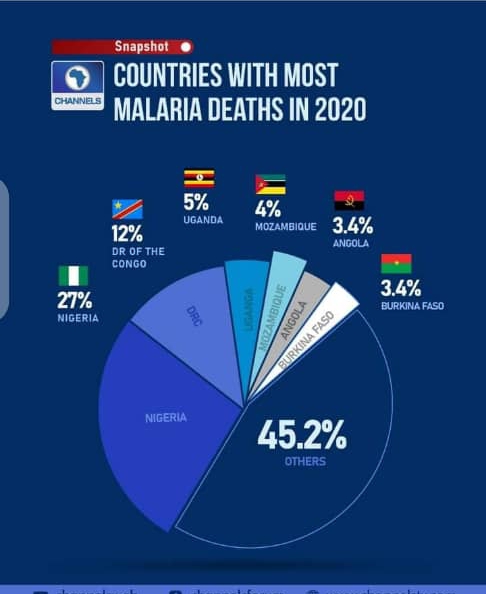
Six African countries accounted for just over half of all malaria deaths worldwide: Nigeria (27%), the Democratic Republic of the Congo (12%), Uganda (5%), Mozambique (4%), Angola (3.4%) and Burkina Faso (3.4%).
Malaria is a life-threatening disease spread to humans by some types of mosquitoes. It is mostly found in tropical countries. It is preventable and curable.
The infection is caused by a parasite and does not spread from person to person.
Symptoms can be mild or life-threatening. Mild symptoms are fever, chills and headache. Severe symptoms include fatigue, confusion, seizures, and difficulty breathing.
Infants, children under 5 years, pregnant women, travellers and people with HIV or AIDS are at higher risk of severe infection.
Malaria can be prevented by avoiding mosquito bites and with medicines. Treatments can stop mild cases from getting worse.
Malaria mostly spreads to people through the bites of some infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. Blood transfusion and contaminated needles may also transmit malaria. The first symptoms may be mild, similar to many febrile illnesses, and difficulty to recognize as malaria. Left untreated, P. falciparum malaria can progress to severe illness and death within 24 hours.